38.01. Xylosandrus crassiusculus (Motschulsky, 1866)
Presence
E: IT SL*
A: ANH BT FUJ GUA GUI HKG HAI HEB HUB HUN HP JA NC NP SC SCH SD SHA SHN TAI UP XIZ YUN ZHE
AFR
AUR
NAR
NTR
ORR
Older catalogs and keys – citations of name
Wood, Bright 1992; Löbl, Smetana 2011.
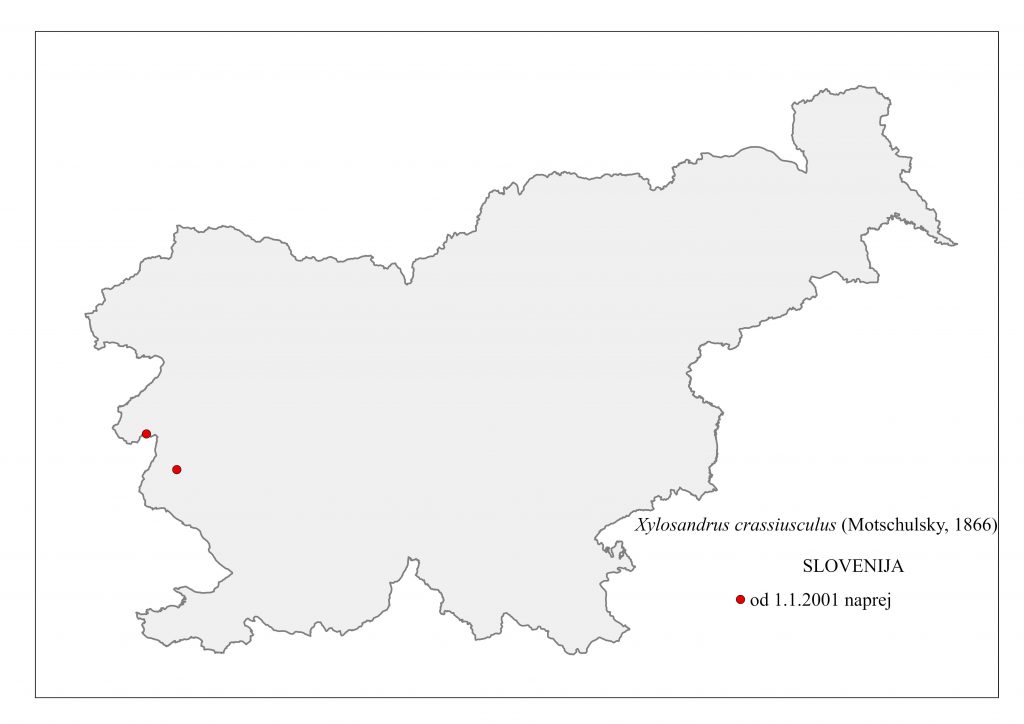
Figure 181: Xylosandrus crassiusculus, distribution map according to historical and recent data
Ecology and presence in Slovenia
A non-native species of Asian origin (Bhutan, Fujian, Sikkim, Nepal, Japan, China, India), it also occurs in Africa, North, Central and South America and Oceania. In Europe, it was first found in 2003 in Tuscany, in a stand of maritime pine (Pinus pinaster) and Turkey oak (Quercus cerris), later spreading to France (2014) and Spain (2016). In Slovenia, the species was recorded in 2017 in Primorska (Podsabotin, Prvačna), in pest monitoring traps (Figure 181). According to literature data, X. crassiusculus is a polyphagous species that inhabits Acacia spp., Alnus spp., Camellia spp., Cocos spp., Coffea spp., Fagus spp., Malus spp., Populus spp., Quercus spp., Salix spp., Ulmus spp., Vitis vinifera and Pinus spp.. It develops two generations per year. Similar to Xylosandrus germanus, it produces a familial planar tunnel system. It ejects droppings from infested trunks in the form of protruding 3-4 cm long rod-shaped formations. The males are 1.5 mm long and the females 3.0 mm. The apex is simply rounded. Ambrosial xylomycetophagous species, the females introduce symbiont fungi of the genus Ambrosiella into the tunnel system.