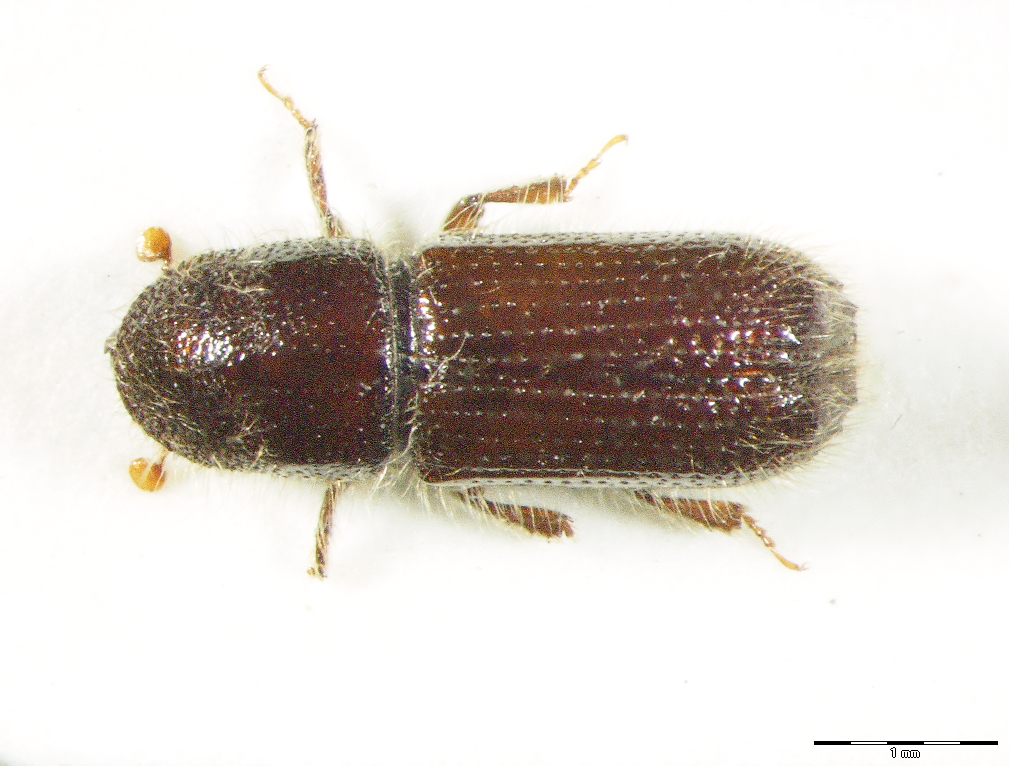
29.04. Orthotomicus proximus (Eichhoff, 1868)
Presence
E: AU BE BH BU BY CR CT CZ DE EN FI FR GE GR HU IT LA LT MD NL NR NT PL PT SK SL SP ST SV SZ UK YU
N: AG
A: ES FE 2FUJ IQ JA KZ MG NC NO SC TR WS »Manchuria«
AFR
ORR
Figure 128: Orthotomicus proximus, dorsal, lateral (Photo: Maja Jurc)
Older catalogs and keys – citations of name
Grüne 1979: Orthotomicus proximus Eichhoff, 1867; Freude, Harde, Lohse 1981: O. proximus Eichhoff (feiferi Keller (1925)); Titovšek 1988: O. proximus (Eichhoff); Pfeffer & Knížek 1993: O. proximus (Eichhoff, 1867); Pfeffer 1995: O. proximus (Eichhoff, 1867).
Figure 129: Orthotomicus proximus, distribution map according to historical and recent data
Ecology and presence in Slovenia
The species is distributed in central and northern Europe, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Bulgaria, the Crimea, the Caucasus, Siberia, Korea, northern China, Japan, northern Africa and Asia, the Afrotropical and Oriental zones. It is rare in Slovenia, having been found only in three sites in the Slovene part of Istria, in Gorenjska and in Koroška (Figure 129). The main hosts are Pinus sylvestris, P. halepensis, P. densiflora, P. koraiensis, P. thunbergiana, P. parviflora, and less frequently Picea spp., Abies spp. and Larix spp.. In Slovenia only one host, P. nigra, has been recorded, in Istria, and specimens have been caught in traps at the other sites. It develops two generations per year, swarming in May and in July and August. They build long star-shaped tunnel systems with 2-5 maternal galleries. Adults are 3.0-3.8 mm long. In both sexes the second denticle is large but not transversely expanded. In the male, all the denticles are on the edge of the apex, but in the female the fourth denticle is pushed inwards so that it is not in line with the others (Figure 128). The species is distinctly secondary, it colonises trunks between 20 and 100 years old.


