28.03. Ips cembrae (Heer, 1836)
Presence
E: AU CT CZ DE FR GB GE GR HU IT LS NL NT PL SK SL SZ
A: FE HEI JA JIL KZ MG SC WS
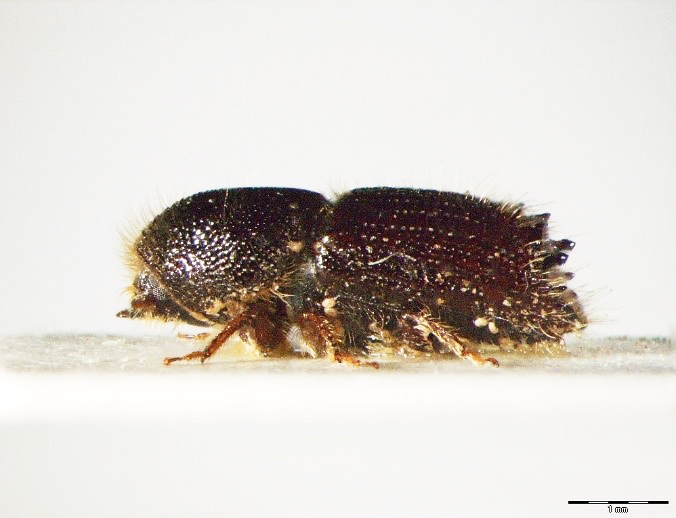
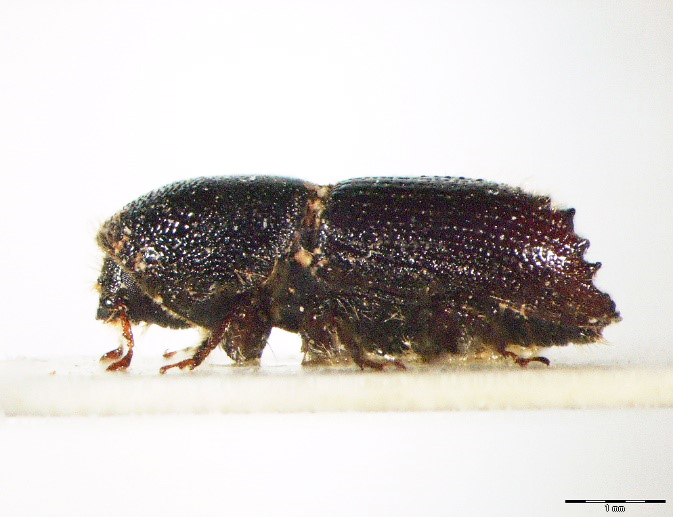
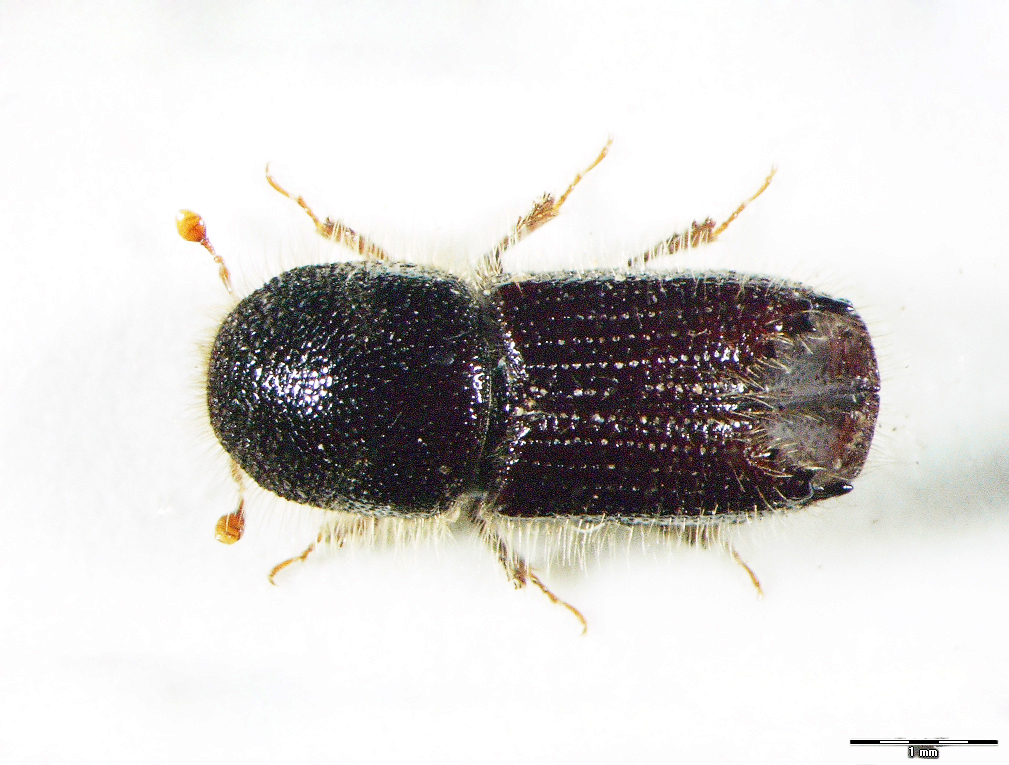
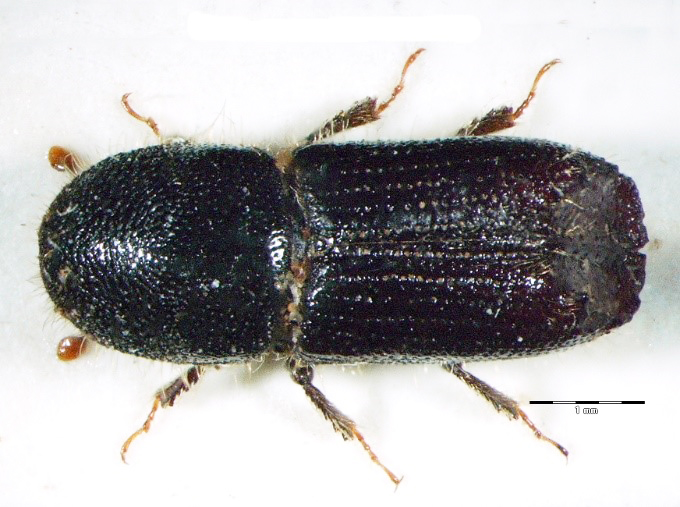
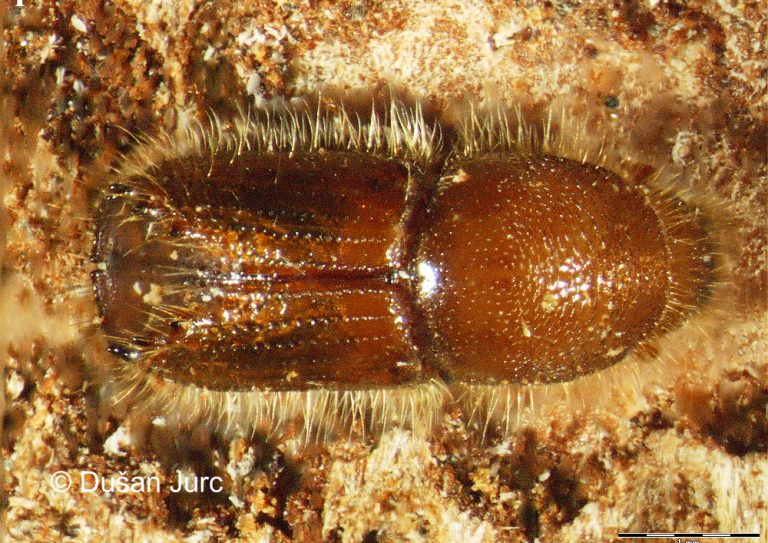
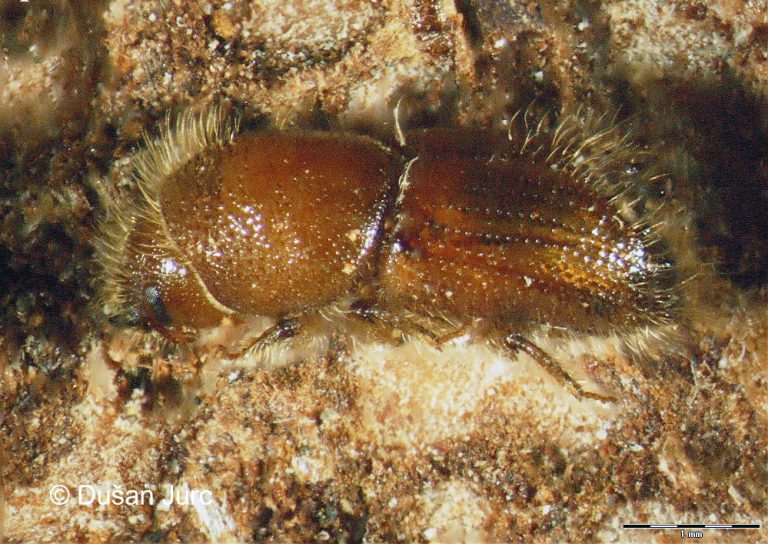
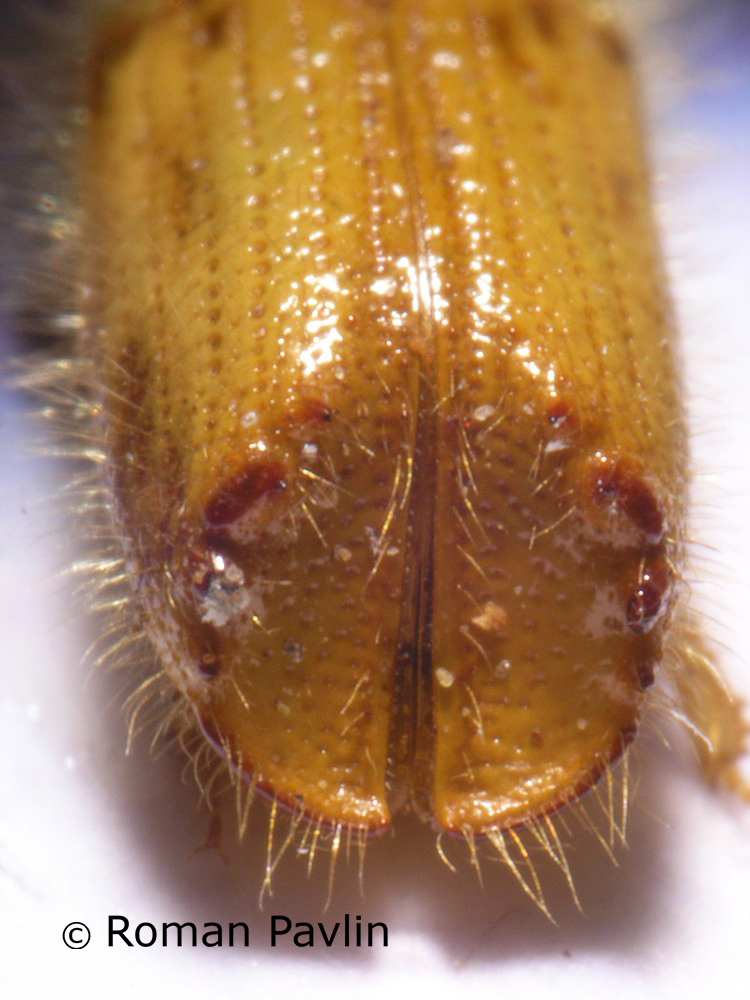
Figure 116: Ips cembrae (above: male – lateral, dorsal, below: female – lateral, dorsal) (Photo: Maja Jurc)
Older catalogs and keys – citations of name
Grüne 1979: Ips cembrae Heer, 1836; Freude, Harde, Lohse 1981: Ips cembrae Heer; Titovšek 1988: Ips cembrae (Heer); Pfeffer & Knížek 1993: I. cembrae (Heer, 1836); Pfeffer 1995: I. cembrae (Heer, 1836).
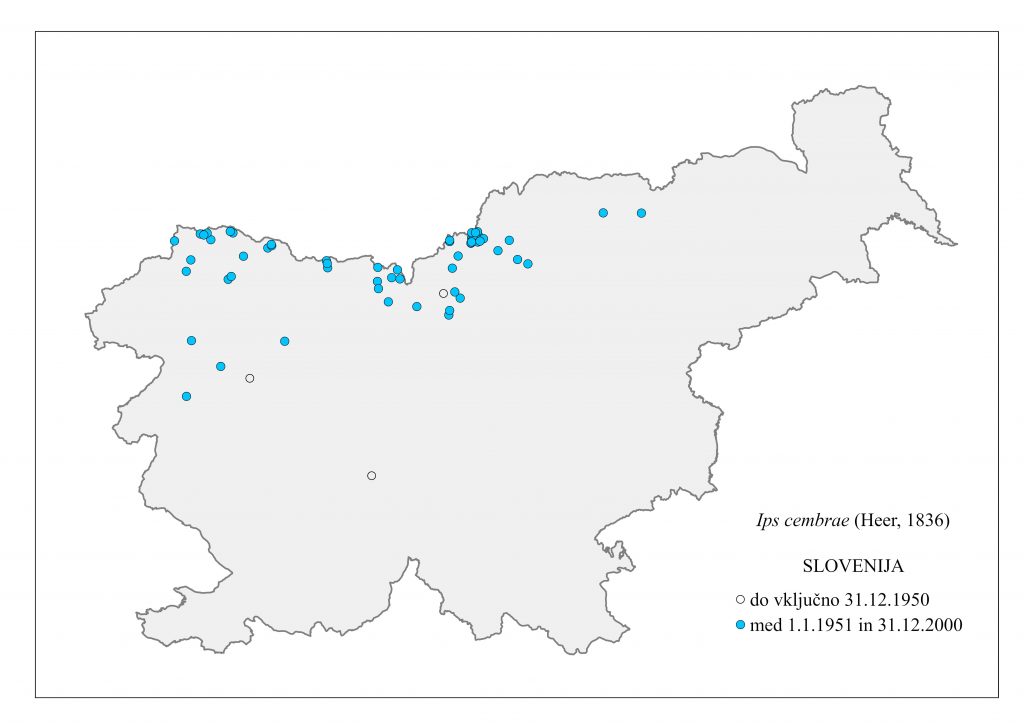
Figure 117: Ips cembrae, distribution map according to historical and recent data
Ecology and presence in Slovenia
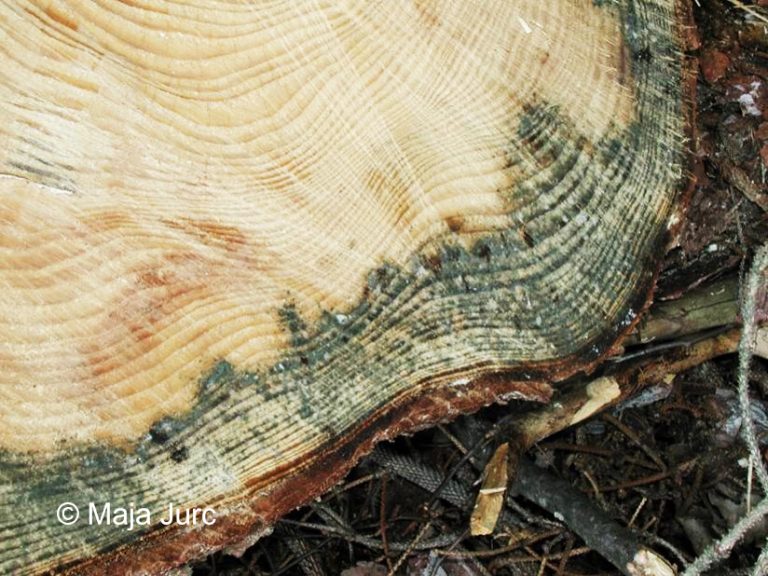
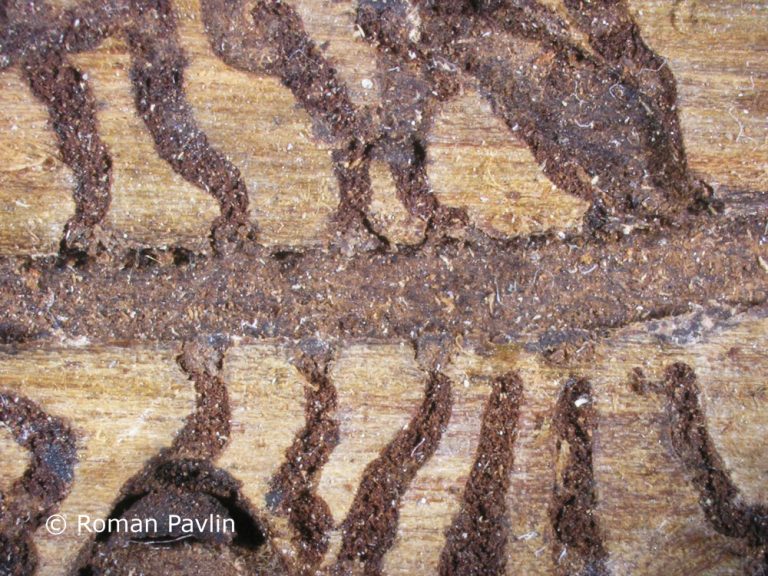
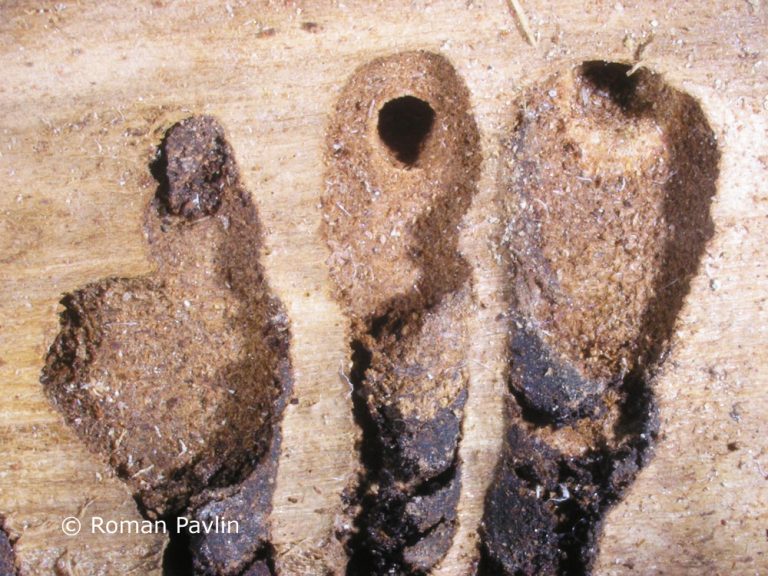
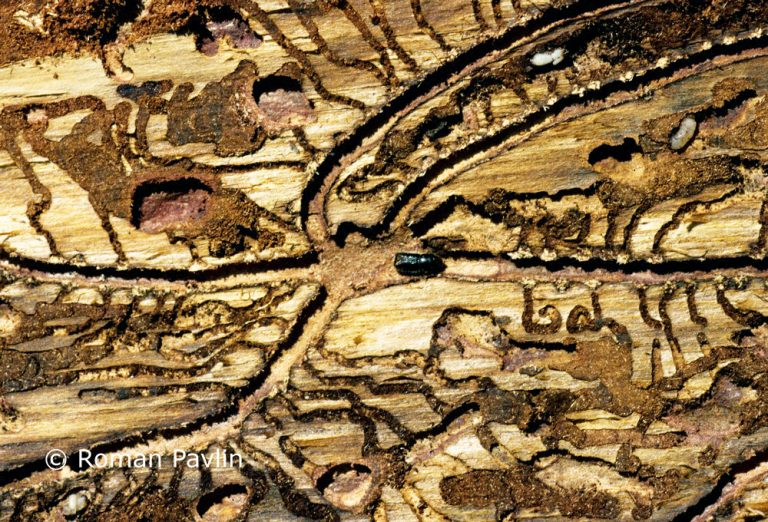
The species is present in western and central Europe, northern Russia, Siberia, the Sakhalin, Korea, Mongolia, Japan and north-western China. The species was considered rare in Slovenia until a systematic census was carried out in 1994-1996 in the northern part of the country partly using synthetic pheromones. The species is found in the montane and subalpine zones of northern Slovenia (Figure 117). Hosts are mainly Pinus cembra, Larix decidua, L. gmelinii and L. sibirica, but it also inhabits Larix leptolepis, Pinus mugo, P. sylvestris, Picea abies, Abies alba and Pseudotsuga menziesii. In Slovenia, the species has been found only on L. decidua and P. abies. Floemophagous, it develops 1-2 generations per year and swarms in late April and July. Longitudinally oriented star-shaped tunnel systems, with 2-4 maternal galleries. Adult length is 4.5-6.0 mm. Both sexes have 4 denticles on the margin of each elytrum, the third being the largest and thickened in a button shape. One row of hairs grows on each side of the shiny tip at the of the elytra (Figure 116). It is a particular threat to larch stands established outside its natural range. Pheromones: Ipsdienol, Ipsenol (3-Methyl-3-buten-1-ol) (Stoakley et al. 1978).