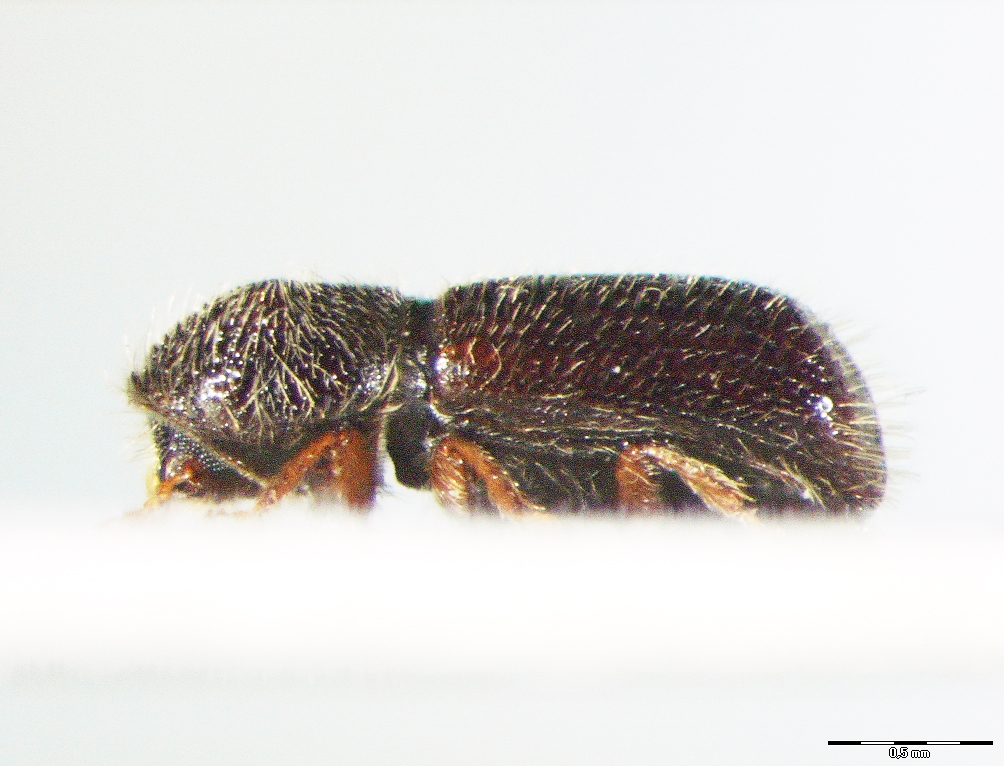
26.01. Taphrorychus bicolor (Herbst, 1794)
Presence
E: AU BE BH BU CR CZ DE FR GB GE HU IT LS LT MC NL NR PL PT RO SL* SK SP SV SZ UK YU »Caucasus«
A: NC SC TR
Figure 105: Taphrorychus bicolor, lateral, dorsal (Foto: Maja Jurc)
Older catalogs and keys – citations of name
Siegel, 1866: Bostrychus autographus Rtzb.; Brancsik, 1871: Dryocetes bicolor Hrbst.; Grüne 1979: Taphrorychus bicolor Herbst, 1793; Freude, Harde, Lohse 1981: Taphrorychus bicolor Herbst; Titovšek 1988: Taphrorychus bicolor (Herbst); Pfeffer & Knížek 1993: Taphrorychus bicolor (Herbst, 1793); Pfeffer 1995: Taphrorychus bicolor (Herbst, 1793).
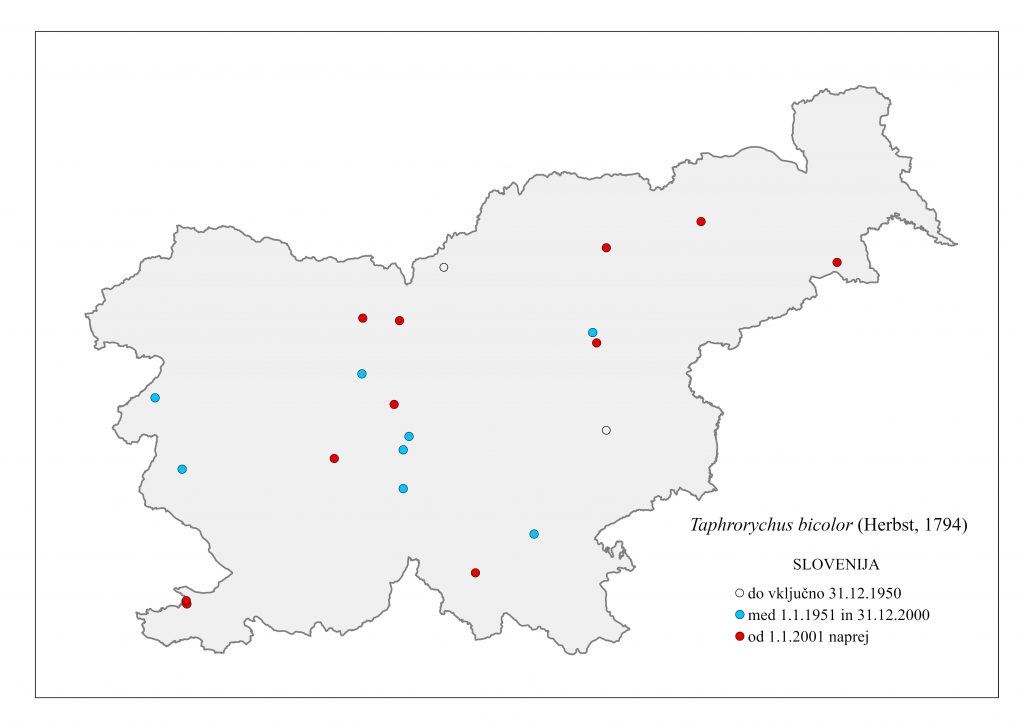
Figure 106: Taphrorychus bicolor, distribution map according to historical and recent data
Ecology and presence in Slovenia
The species is distributed in Europe, in the Crimea, the Caucasus, Turkey, North Korea, and South Korea; Siegel (1866) and Brancsik (1871) state for Carniola and Styria that the species was “rare, under the bark of beech”. Especially after 1990, the species has been found at sites in most of Slovenia, but it is not common (Figure 106). Hosts include Fagus sylvatica, F. orientalis, less frequently also Carpinus betulus, C. orientalis, Quercus pedunculata, Q. petraea, Q. pontica, Populus tremula, Betula spp., Juglans regia and Acer pseudoplatanus. In Slovenia it is found only on F. sylvatica, more often caught in traps. Develops two generations per year, the first swarming in March and April, the second in June. The tunnel system is irregularly branched, including the larval tunnels, resembling a labyrinth. Adult length is 1.6-2.5 mm (Figure 105).





